Supervised Learning - Linear Regression Cost Function Intuition
Abstract
Cost Function or Residual Sum of Squares (RSS)
J(θ0,θn)=∑i=1 ei2 = 1/2m∑i=1 (y^i−yi)2=1/2m∑i=1 (hθ(xi)−yi)2
Where
hθ(xi)=y^i = θ0+ θ1 x1 +..+ θn xn is the predictor of the ith value of Y th based on the ith value of X.
The criteria for optimization problem is
Minimize J(θ0,θn)=1/2m∑i=1 (y^i−yi)2. is also known as the least squares criteria.
Questions:
1.Why to optimize J(θ0,θn) using the residual sum of squares instead of Absolute Value of the sum of residuals: 1/2m∑i=1 |(y^i−yi)|
Answer: even although, both math work to calculate the residual error, computationally speaking, it is more expensive to run a formula with Absolute Value.
2.Why not to optimize J(θ0,θn) as the sum of the residuals: 1/2m∑i=1 (y^i−yi)
Answer: J(θ0,θn) could be 0 beacuse some negative residuals might cancel some positive residuals
3. Why 1/2m on J(θ0,θn)?
Answer: The term 1/m is due to J(θ0,θn) is an average of the residuals. The term 1/2 is to make easier the computation of the partial derivative when we proceed to minimize it.
Example of Cost Function
For simplicity sake, we will show in Python the Visual representation of a cost function for a univariate model:
hθ(xi)=y^i = θ0+ θ1 x1
J(θ0,θ1) = 1/2m∑i=1 (hθ(xi)−yi)2
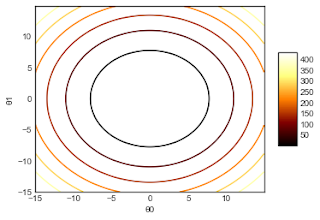
Here, the respective contour maps generated from Python
Author: Eduardo Toledo - MSc in Economic Sciences , Spec. Project Management and Software Engineer
Eduardo Toledo Data Science Blog
'''
======================
3D surface (color map)
======================
======================
3D surface (color map)
======================
Demonstrates plotting a 3D surface colored with the coolwarm color map.
The surface is made opaque by using antialiased=False.
The surface is made opaque by using antialiased=False.
Also demonstrates using the LinearLocator and custom formatting for the
z axis tick labels.
'''
z axis tick labels.
'''
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import cm
from matplotlib.ticker import LinearLocator, FormatStrFormatter
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import cm
from matplotlib.ticker import LinearLocator, FormatStrFormatter
import numpy as np
def f(theta0, theta1):
return theta0**2 + theta1**2
return theta0**2 + theta1**2
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.gca(projection='3d')
ax = fig.gca(projection='3d')
# Make data.
theta0 = np.arange(-15, 15, 0.1)
theta1 = np.arange(-15, 15, 0.1)
Theta0, Theta1 = np.meshgrid(theta0, theta1)
theta0 = np.arange(-15, 15, 0.1)
theta1 = np.arange(-15, 15, 0.1)
Theta0, Theta1 = np.meshgrid(theta0, theta1)
J = f(Theta0,Theta1)
# Plot the surface.
surf = ax.plot_surface(Theta0, Theta1, J, cmap=cm.afmhot,
linewidth=0, antialiased=False)
ax.set_zlabel("J(θ0,θ1)")
# Plot the surface.
surf = ax.plot_surface(Theta0, Theta1, J, cmap=cm.afmhot,
linewidth=0, antialiased=False)
ax.set_zlabel("J(θ0,θ1)")
# Add a color bar which maps values to colors.
fig.colorbar(surf, shrink=0.5, aspect=5)
plt.xlabel("θ0")
plt.ylabel("θ1")
fig.colorbar(surf, shrink=0.5, aspect=5)
plt.xlabel("θ0")
plt.ylabel("θ1")
plt.show()
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import axes3d
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import cm
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
cset = ax.contour(Theta0, Theta1, J, cmap=cm.afmhot)
fig.colorbar(surf, shrink=0.5, aspect=5)
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
cset = ax.contour(Theta0, Theta1, J, cmap=cm.afmhot)
fig.colorbar(surf, shrink=0.5, aspect=5)
#ax.clabel(cset, fontsize=9, inline=1)
plt.xlabel("θ0")
plt.ylabel("θ1")
ax.set_zlabel("J(θ0,θ1)")
plt.xlabel("θ0")
plt.ylabel("θ1")
ax.set_zlabel("J(θ0,θ1)")
plt.show()
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.style.use('seaborn-white')
import numpy as np
plt.style.use('seaborn-white')
import numpy as np
#plt.contour(X, Y, Z, colors='black');
plt.contour(Theta0, Theta1, J, cmap=cm.afmhot);
plt.colorbar(surf, shrink=0.5, aspect=5)
plt.xlabel("θ0")
plt.ylabel("θ1")
plt.contour(Theta0, Theta1, J, cmap=cm.afmhot);
plt.colorbar(surf, shrink=0.5, aspect=5)
plt.xlabel("θ0")
plt.ylabel("θ1")




Comments
Post a Comment